America has a major dependency problem. In recent decades, there’s been a significant increase in the number of working-age adults relying on handouts.
This is bad news for poor people and bad news for taxpayers.  But it’s also bad news for the nation since it reflects an erosion of societal capital.
But it’s also bad news for the nation since it reflects an erosion of societal capital.
For all intents and purposes, people are being paid not to be productive.
Guided by the spirit of Calvin Coolidge, we need to reform the welfare state.
Professor Dorfman of the University of Georgia, in a column for Forbes, pinpoints the core problem.
The first failure of government welfare programs is to favor help with current consumption while placing almost no emphasis on job training or anything else that might allow today’s poor people to become self-sufficient in the future.
…It is the classic story of giving a man a fish or teaching him how to fish. Government welfare programs hand out lots of fish, but never seem to teach people how to fish for themselves. The problem is not a lack of job training programs, but rather the fact that the job training programs fail to help people. In a study for ProPublica, Amy Goldstein documents that people who lost their jobs and participated in a federal job training program were less likely to be employed afterward than those who lost their jobs and did not receive any job training. That is, the job training made people worse off instead of better. …Right now, the government cannot teach anyone how to find a fish, let alone catch one.
And Peter Cove opines on the issue for the Wall Street Journal.
…the labor-force participation rate for men 25 to 54 is lower now than it was at the end of the Great Depression. The welfare state is largely to blame. More than a fifth of American men of prime working age
are on Medicaid. According to the Census Bureau, nearly three-fifths of nonworking men receive federal disability benefits. The good news is that the 1996 welfare reform taught us how to reduce government dependency and get idle Americans back to work. …Within 10 years of the 1996 reform, the number of Americans in the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program fell 60%.
Interestingly, European nations seem to be more interested in fixing the problem, perhaps because they’ve reached the point where reform is a fiscal necessity.
Let’s look at what happened when the Dutch tightened benefit rules.
A fascinating new study from economists in California and the Netherlands sheds light on how welfare dependency is passed from one generation to the next – and how to save children from lives of idleness.
A snowball effect across generations could arise if welfare dependency is transmitted from parents to their children, with potentially serious consequences for the future economic situation of children. …there is little evidence on whether this relationship is causal.
Testing for the existence of a behavioural response, where children become benefit recipients because their parents were, is difficult… Our work overcomes these identification challenges by exploiting a 1993 reform in the Dutch Disability Insurance (DI) programme… The 1993 reform tightened DI eligibility for existing and future claimants, but exempted older cohorts currently on DI (age 45+) from the new rules. This reform generates quasi-experimental variation in DI use… Intuitively, the idea is to compare the children of parents who are just over 45 years of age to children whose parents are just under 45. .
Here’s the methodology of their research.
The first step is to understand the impact of the 1993 reform on parents. Figure 1 shows that parents who were just under the age 45 cut-off, and therefore subject to the harsher DI rules, are 5.5 percentage points more likely to exit DI by the year 1999 compared to parents just over the age 45 cut-off. These treated parents saw a 1,300 euro drop in payments on average. …the reform changed other outcomes as well. There is a strong rebound in labour earnings.
This chart from their research captures the discontinuity.
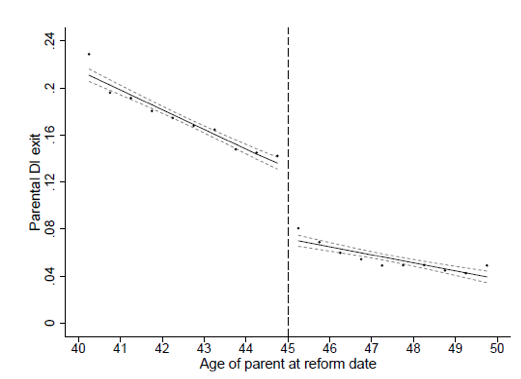
Here are the main results.
The second step is to see how children’s DI use changed based on whether the reform affected their parents. We measure a child’s cumulative use of DI as of 2014, by which time they are 37 years old on average. Figure 2 reveals a noticeable jump in child DI participation at the parental age cut-off of 45. There is an economically significant 1.1 percentage point drop for children if their parent was exposed to the reform, which translates into an 11% effect relative to the mean child participation rate of 10%. …welfare cultures, defined as a causal intergenerational link, exist.
This second chart illustrates the positive impact.
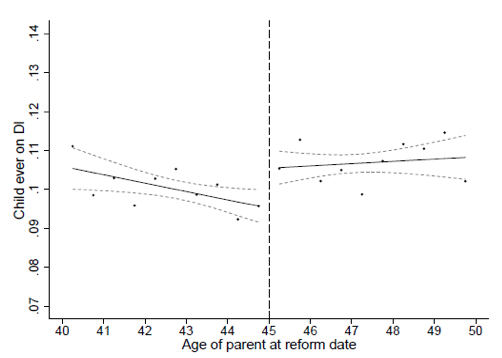
But here’s the most important part of the research.
Reducing access to redistribution to parents is a good way of boosting income and education for children.
…we examine whether a child’s taxable earnings and participation in other social support programmes change. Cumulative earnings up to 2014 rise by approximately €7,200 euros, or a little less than 2%, for children of parents subject to the less generous DI rules. In contrast, we find no detectable change in cumulative unemployment insurance receipt, general assistance (i.e. traditional cash welfare), or other miscellaneous safety net programs. Looking at a child’s educational attainment, there is intriguing evidence for anticipatory investments. When a parent is subject to the reform which tightened DI benefits, their child invests in 0.12 extra years of education relative to an overall mean of 11.5 years. …these findings provide suggestive evidence that children of treated parents plan for a future with less reliance on DI in part by investing in their labour market skills.
And it’s also worth noting that taxpayers benefit when welfare eligibility is restricted.
These strong intergenerational links between parents and children have sizable fiscal consequences for the government’s long term budget. Cumulative DI payments to children of the targeted parents are 16% lower. This is a substantial additional saving for the government’s budget, especially since there is no evidence that children substitute these reductions in DI income for additional income from other social assistance programmes. Furthermore, there is a fiscal gain resulting from the increased taxes these children pay due to their increased labour market earnings. Overall, we calculate that through the year 2013, children account for 21% of the net fiscal savings of the 1993 Dutch reform in present discounted value terms. This share is projected to increase to 40% over time.
Ryan Streeter of American Enterprise Institute explains that other European nations also are reforming.
Welfare reformers might draw some lessons from unlikely places, such as Scandinavia. While progressives like to uphold Nordic democratic socialism as a model for America, the Scandinavian welfare systems are arguably more pro-work than ours… For instance, to deal with declining labor force participation,
Denmark eliminated permanent disability benefits for people under 40 and refashioned its system to make employment central. Sweden reformed its welfare system to focus on rapid transitions from unemployment to work. Their program lowers jobless assistance the longer one is on welfare. The Nordic model is more focused on eliminating reasons not to work such as caregiving or lack of proper training than providing income replacement. Similarly, the British government combined six welfare programs with varying requirements into a single “universal credit.” The benefit is based on a sliding scale and decreases as a recipient’s earnings increase, replacing several differing formulas for phasing out of welfare programs with one. An evaluation of the new program, which encourages work, found that 86 percent of claimants were trying to increase their work hours and 77 percent were trying to earn more, compared to 38 percent and 55 percent, respectively, under the previous system. …Scandinavia and Britain learned a while ago that successful welfare reform is not just about how much money a country spends on people who earn too little. It’s really about how to help them find and keep a good job. It’s time for America to catch up.
Amen.
For what it’s worth, I think we’ll be most likely to get good results if we get Washington out of the redistribution business.
In effect, block grant all means-tested programs to the states and then phase out the federal funding. That would give states the ability to experiment and they could learn from each other about the best way of helping the truly needy while minimizing incentives for idleness.

