A couple of weeks ago, I offered some guarded praise for Paul Ryan’s budget, pointing out that it satisfies the most important requirement of fiscal policy by restraining spending – to an average of 3.1 percent per year over the next 10 years – so that government grows slower than the productive sector of the economy (I call this my Golden Rule).
I was more effusive in my comments about Senator Rand Paul’s budget, which limited the growth of the federal budget over the next 10 years to an average of 2.2 percent each year.
Now the Republican Study Committee from the House of Representatives has put forth a plan that also deserves considerable applause. Like Senator Paul, the RSC plan would impose immediate significant fiscal discipline such that spending in 2017 would be about the same level as it is this year.
Think of this as being similar to the very successful fiscal reforms of New Zealand and Canada in the 1990s.
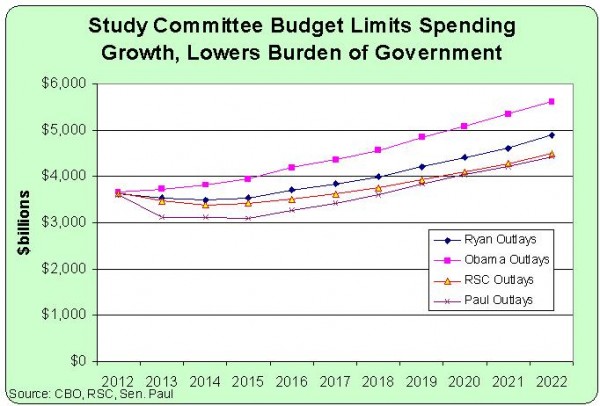
After the initial period of spending restraint, the budget would be allowed to grow, but only about as fast as the private economy. This chart shows spending levels for the Obama budget, the Paul Ryan budget, the Rand Paul budget, and the RSC budget.
A couple of final points.
1. For all the whining and complaining from the pro-spending lobbies, the RSC budget is hardly draconian. Federal spending, measured as a share of GDP, would only drop to where it was when Bill Clinton left office.
2. One preferable feature of the Rand Paul budget is that the Kentucky Senator eliminates four needless and wasteful federal departments – Commerce, Education, Energy, and Housing and Urban Development. As far as I can tell, no departments are eliminated in the RSC plan. Also, Senator Paul’s plan is bolder on tax reform, scrapping the corrupt internal revenue code and replacing it with a simple and fair flat tax.
3. The RSC comes perilously close to winning a Bob Dole Award. The first chapter of their proposal fixates on symptoms of debt and deficits rather than the real problem of excessive government spending. Indeed, the first six charts all relate to deficits and debt, creating an easy opening for leftists to say they can solve the mis-defined problem with higher taxes.
There are lots of other details worth exploring, but the main lesson is that restraining spending is the key to good fiscal policy.
And that’s what’s happening. Indeed, the good news is that policymakers have proposed several budget plans that would shrink the burden of spending as a share of GDP. It’s refreshing to debate the features of several good plans (rather than comparing the warts in the competing plans during the big-government Bush years).
The bad news is that Harry Reid and Barack Obama will succeed in blocking any progress this year, so America will move ever closer to becoming another Greece.